AI is that tiny stuff with chunky plugs that has crept into everyday lives sooner than we expected. It has become a quintessential, more proactive than Google (that is generic); but AI generated responses are more personalized, because you prompt that way. The idea of conversational, professional, assertive, direct, indirect, interrogative, Humorous, Witty, Inquisitive, Socratic, Narrative, Storytelling, Assertive, Bold, Analytical, Data-driven, Inspirational, Visionary, Critical, Reflective, Meta, Playful can turn a conversation unexpectedly, which Google isn’t able to do.
I heard of data scientists, I heard of people with Python – Java and ML skills, but no sooner you ask GPT to prompt, and you will become as good as an AI developer without a relevant degree. Over-reliance on AI tools diminishes problem-solving skills, a persistent skills gap in emerging AI domains, and challenges in implementing AI solutions can pose a challenge for an AI developer.
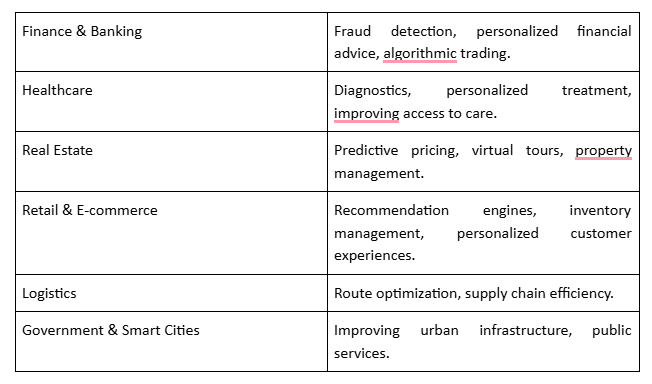
Right now, the most tangible real-world example at home is ambient computing devices like e-readers, smart sensors, and remote controls that stay perpetually powered by harvesting ambient wireless electricity from across the room. It’s a smart thing, but these things always begin small. It is beneficial to Hire AI developers in the UAE as they are highly skilled in (1) NLP, (2) Computer Vision, (3) Predictive Analytics, and (4) Generative AI (LLMs), powering digital transformation across Finance, Healthcare, Real Estate, Retail, and Logistics, solving complex problems from automation to personalized experiences;
Skills They Possess
Does an exceptional AI developer simply write great code, or do they combine technical depth with curiosity, communication, and resilience?
In the UAE, hiring AI developers faces challenges like a shortage of deep-skilled talent, fierce competition, and verifying true competence vs. hype, alongside significant concerns over data bias, privacy, and accountability in AI systems, demanding developers build transparent, ethical, and locally compliant (Arabic/English) solutions for the diverse market, especially with UAE government pushes for AI-driven Emiratization, notes Bayt.com Specialties.
Hiring Models
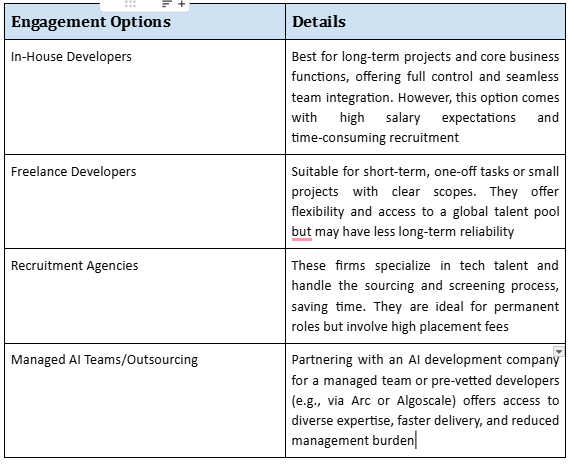
Businesses can choose from several hiring models based on their project scope, budget, and long-term goals:
There is always a process to hire
Ascertain the problem at hand, which technologies will be used, which professional networks should be used (LinkedIn, GitHub, Stack Overflow), and screen candidates by reviewing their portfolio, past projects, and real-world applications; Conduct technical assessments and live coding challenges. Assess soft skills and cultural fit by asking behavioral questions, and making them interact with the team. Extend an offer, in line with the competitors, and ensure a smooth onboarding process with clear goals, access to necessary tools, and mentorship opportunities.
What tends to stay on your mind when you are bringing an AI developer on board in the UAE?
The UAE has become a fast-growing hub for AI, but that growth brings its own set of complications. Developers who want to succeed here need more than technical depth. They need a solid grip on Responsible AI, ethical data use, and the ability to adapt tools for both Arabic and English audiences.
Skilled ML engineers and data scientists are in high demand, and the number of genuinely experienced professionals has not yet caught up. As a result, hiring often takes longer and becomes more competitive than expected.
Another issue is how difficult it can be to separate those with real expertise from those who only speak about AI at a surface level. Companies should not rely solely on verbal communication, but must check the skills on multiple levels, via practical tests and working models.
Developers need to have a working knowledge of UAE local language – Arabic and English and build systems that understand local culture, regulations, and business behavior. This applies across all business domains, all industries.
Take care of data security, compliance by all the regulations, government rules, and development best practices.
Integrating AI into existing ecosystems is not easy. Tools must work smoothly with CRMs, e-commerce systems, WhatsApp channels, voice platforms, and whatever else a business already uses.
The UAE market is dynamic and demands solutions that can grow and evolve. Generic, off the shelf products seldom meet that requirement.
Unlock Business Potential with Experient AI Development Services
Hiring skilled AI developers helps businesses leverage the power of AI. What do I mean by that? They can automate repetitive tasks and enhance resource management. They can build
custom solutions like recommendation engines, chatbots, and predictive analytics that provide a competitive advantage. They get to decide when they are left with time, because the AI-backed script already does the heavy lifting. When the outcome is accurate, timely, and without any errors, beyond expectations, then the customer experience is already high.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the average cost to hire an AI developer?
Costs vary significantly by experience, location, and the hiring model used (freelance, full-time, or agency). Full-time mid-level developers in the US might command annual salaries upward of $130,000, while freelance rates can range from $25-$150+ per hour.
- How long does it typically take to hire an AI developer?
The process can take several weeks to a few months for in-house hires. Utilizing specialized agencies or pre-vetted talent platforms can significantly reduce this time, often to days or a couple of weeks.
- What qualifications should I look for in an AI developer?
Prioritize strong programming skills (Python), knowledge of ML/DL frameworks (TensorFlow, PyTorch), data handling proficiency, problem-solving skills, and the ability to work collaboratively. Real-world project experience often outweighs academic certificates.




